ケミカルバイオロジー研究グループ(終了)
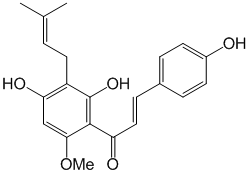
Xanthohumol
- Structure
-

- Producing organism
- Humulus lupulus
- Biological activity
- valosin-containing protein inhibitor
- Abstract
- Autophagy is a bulk, nonspecific protein degradation pathway that is involved in the pathogenesis of cancer and neurodegenerative disease. Here, we observed that xanthohumol (XN), a prenylated chalcone present in hops (Humulus lupulus L.) and beer, modulates autophagy. By using XN-immobilized beads, valosin-containing protein (VCP) was identified as a XN-binding protein. VCP has been reported to be an essential protein for autophagosome maturation. Using an in vitro pull down assay, we showed that XN bound directly to the N domain, which is known to mediate cofactor and substrate binding to VCP. These data indicated that XN inhibited the function of VCP, thereby allowing the impairment of autophagosome maturation and resulting in the accumulation of microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3-II (LC3-II). This is the first report demonstrating XN as a VCP inhibitor that binds directly to the N domain of VCP. Our finding that XN bound to and inactivated VCP not only reveals the molecular mechanism of XN-modulated autophagy but may also explain how XN exhibits various biological activities that have been reported previously.
- References
-
- Sasazawa Y, Kanagaki S, Tashiro E, Nogawa T, Muroi M, Kondoh Y, Osada H, Imoto M.: Xanthohumol impairs autophagosome maturation through direct inhibition of valosin-containing protein.
ACS Chem Biol, 7(5): 892-900 (2012) [ doi: 10.1021/cb200492h ]
[ doi: 10.1021/cb200492h ] - Sasazawa Y, Kanagaki S, Tashiro E, Nogawa T, Muroi M, Kondoh Y, Osada H, Imoto M.: Xanthohumol impairs autophagosome maturation through direct inhibition of valosin-containing protein.