化合物アレイによる小分子化合物とタンパク質の物理的相互作用の解析
化合物アレイによる小分子化合物とタンパク質の物理的相互作用の解析
概要
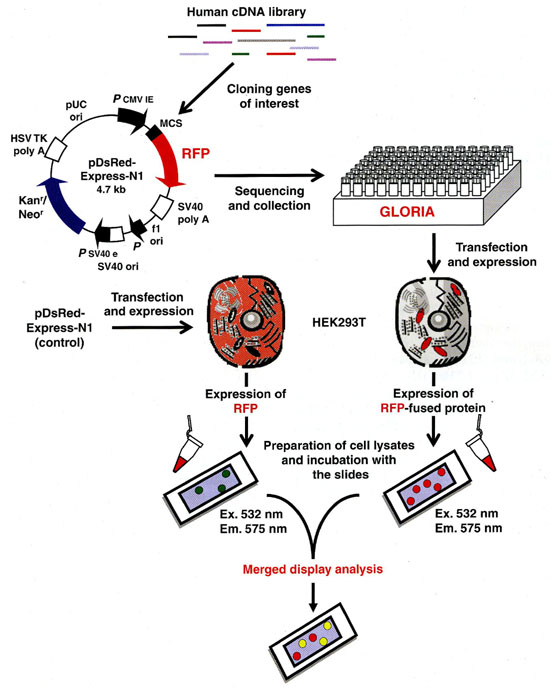
小分子化合物をスライドガラスに固定化した化合物アレイを用いて、目的タンパク質と相互作用する小分子化合物の探索を行う。化合物の固定化は、光親和型固定化法により行うため、化合物に特定の官能基を必要としない。また、1枚のスライドガラスに2300種類の化合物をDuplicateで固定化することができる。
その他:化合物の数が1000以上まとまっていれば、単独で化合物アレイを作製することが可能である。化合物の数が少ない場合は、化合物が集まった段階で化合物アレイを作製するため、作製までに時間を必要とする。
 |
|
Overview of Systematic Chemical Array Screening Method. |
References:
-
I. Miyazaki, S. Simizu, H. Ichimiya, M. Kawatani, H. Osada.
Robust and systematic drug screening method using chemical arrays and protein library: Identification of novel inhibitors of carbonic anhydrase II.
Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 72, 2739-2749 (2008). -
N. Kanoh, A. Asami, M. Kawatani, K. Homda, S. Kumashiro, H. Takayama, S. Shimizu, T. Amemiya, Y. Kondoh, S. Hatakeyama, K. Tsuganezawa, R. Utata, A. Tanaka, S. Yokoyama, H. Tashiro, H. Osada.
Photo-cross-linked small-molecule microarrays as chemical genomic tools for dissecting protein-ligand interactions.
Chem.Asian J., 1, 789-797 (2006). -
N. Kanoh, S. Kumashiro, S. Simizu, Y. Kondoh, S. Hatakeyama, H. Tashiro, H. Osada.
Immobilization of natural products on glass slides by using a photoaffinity reaction and the detection of protein-small-molecule interactions.
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 42, 5584-5587 (2003).