Polyoxin A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M
Structure
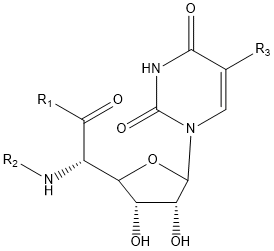
| Polyoxin | R1 | R2 | R3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 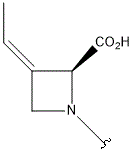 |
 |
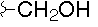 |
B | 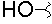 |
 |
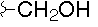 |
| C | 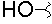 |
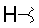 |
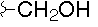 |
|
| D | 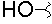 |
 |
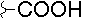 |
|
| E | 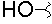 |
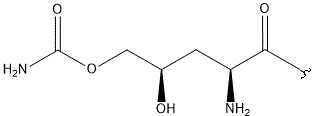 |
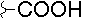 |
F |  |
 |
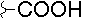 |
| G | 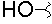 |
 |
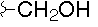 |
|
| H |  |
 |
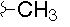 |
|
| I | 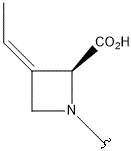 |
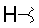 |
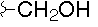 |
|
| J | 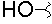 |
 |
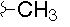 |
|
| K |  |
 |
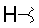 |
|
| L | 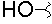 |
 |
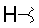 |
|
| M | 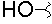 |
 |
 |
- Producing organism
- Streptomyces cacaoi var. asoensis
- Biological activity
- fungal cell wall synthesis inhibition
- Abstract
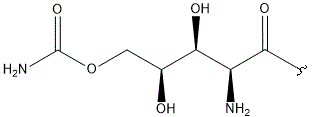
- Polyoxin A-M were found to be a new class of peptide nucleosides. Hydrolytic degradation of polyoxins afforded three groups of unusual α-L-amino acids, i.e., 1-(5'-amino-5'-deoxy-β-D-allofuranuronosyl)-5-hydroxymethyluracil (polyoxin C) or its three nucleobase analogs, 5-O-carbamoyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-L-xylonic acid or its 3-deoxy analog, and 3-ethylidene-L-azetidine-2-carboxylic acid. These structures were established on chemical and spectoroscopic evidence. 5'-Aminofuranuronoside common to all polyoxins constitutes a nucleoside with α-amino acid nature. Sequence analysis showed polyoxins are di- or tripeptide of these moieties. The structures so elucidated embody all the interesting chemical features of polyoxins.
- References
-
isolation and structural determination
- Isono K, Asahi K, Suzuki S.: Studies on polyoxins, antifungal antibiotics. 13. The structure of polyoxins.
J Am Chem Soc, 91(26): 7490-7505 (1969)
- Shibuya K, Tanaka M, Nanbata T, Isono K, Suzuki S.: Transformation of Polyoxins D, E, and F with Sodium Bisulfite.
Agric Biol Chem, 36(7): 1229-1236 (1972) [ doi: 10.1271/bbb1961.36.1229 ]- Isono K and Suzuki S.: The Polyoxins: Pyrimidine Nucleoside Peptide Antibiotics Inhibiting Fungal Cell Wall Biosynthesis.
Heterocycles, 13(1): 333-351(1979) [ doi: 10.3987/S-1979-01-0333 ]- Hanessian S, Fu JM, Tu Y, Isono K.: Structural identity and stereochemical revision of polyoximic acid.
Tetrahedron Lett, 34(26): 4153-4156 (1993) [ doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)60515-4 ] - Isono K, Asahi K, Suzuki S.: Studies on polyoxins, antifungal antibiotics. 13. The structure of polyoxins.