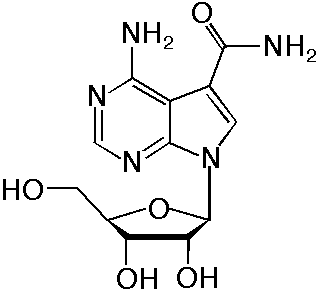
Sangivamycin
- Structure
-
 (Re-discovered compound)
(Re-discovered compound)
- Producing organism
- Streptomyces sp.
- Biological activity
- inhibitor of protein kinase C
- Abstract
- During the screening for the inhibitors of protein kinase C (PKC), we found that a streptomycete produced an inhibitor in our bleb-forming assay (Osada et al., J. Antibiotics 41: 925, 1988). The inhibitor was isolated and identified as sangivamycin (4-amino-5-carboxamide-7-(D-ribofuranosyl)pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine). Biological activity of sangivamycin was compared with that of other 7-deazaadenosine group antibiotics, tubercidin and toyocamycin. Sangivamycin showed a strong inhibitory activity against bleb-formation of K562 cells and PKC. On the other hand, tubercidin and toyocamycin had only weak activities in both assays. This paper deals with a new biological activity of sangivamycin, that of an inhibitor of protein kinases, especially PKC.
- References
-
isolation and structural determination
- Rao KV.: Structure of sangivamycin.
J Med Chem, 11(5): 939-941 (1968) biological activity
biological activity- Osada H, Sonoda T, Tsunoda K, Isono K.: A new biological role of sangivamycin; inhibition of protein kinases.
J Antibiot, 42(1): 102-106 (1989)
- Rao KV.: Structure of sangivamycin.