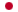
RK-1441A, B
- Structure
-
- Producing organism
- Streptomyces sp.
- Biological activity
- antibacteriophage activity
- Abstract
- Streptomyces griseus and bacteriophage B were used for an assay system detecting anti-bacteriophage antibiotics. Streptomyces sp. RK-1441 was found to produce antibacteriophage antibiotics, RK-1441A and B, which are pyrrolo[1,4]benzodiazepine group antibiotics related to neothramycin. Both RK-1441A and B had antibacteriophage activity. The former showed antimicrobial activity on a hypersensitive strain of E. coli for antitumor antibiotics, but the later did not show the activity. Restriction enzyme assay suggested that RK-1441A formed adducts with guanine residues in DNA strands. RK-1441B was not active in vitro, but it might be converted to the active form in host organisms.
- References
-
isolation and structural determination
- Osada H, Ishinabe K, Yano T, Kajikawa K, Isono K.: New pyrrolobenzodiazepine antibiotics, RK-1441A and B. I. Biological properties.
Agric Biol Chem, 54(11): 2875-2881 (1990)
- Osada H, Ishinabe K, Yano T, Kajikawa K, Isono K.: New pyrrolobenzodiazepine antibiotics, RK-1441A and B. I. Biological properties.