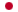
RK-286C, D
- Structure
-
- Producing organism
- Streptomyces sp. RK-286
- Biological activity
- protein kinase C inhibitor
- Abstract
- A newly isolated strain of Streptomyces sp. produces a new nucleoside antibiotic, ascamycin and the corresponding dealanyl derivative. The structure of ascamycin was determined to be 2-chloro-9-β-[5-O-(N-L-alanyl)sulfamoyl-D-ribofuranosyl]-adenine. Remarkable selective toxicity of ascamycin compared to the dealanyl derivative was accounted for on the basis of a dealanylating enzyme present in the envelope of sensitive bacteria. After dealanylation, it becomes permeable to cell membrane.
- References
-
isolation and structural determination
- Osada H, Takahashi H, Tsunoda K, Kusakabe H, Isono K.: A new inhibitor of protein kinase C, RK-286C (4'-demethylamino-4'-hydroxystaurosporine). I. Screening, taxonomy, fermentation and biological activity.
J Antibiot, 43(2): 163-167 (1990)
- Takahashi H, Osada H, Uramoto M, Isono K.: A new inhibitor of protein kinase C, RK-286C (4'-demethylamino-4'-hydroxystaurosporine). II. Isolation, physico-chemical properties and structure.
J Antibiot, 43(2): 168-173 (1990)
- Osada H, Satake M, Koshino H, Onose R, Isono K.: A new indolocarbazole antibiotic, RK-286D.
J Antibiot, 45(2): 278-279 (1992)
- Osada H, Takahashi H, Tsunoda K, Kusakabe H, Isono K.: A new inhibitor of protein kinase C, RK-286C (4'-demethylamino-4'-hydroxystaurosporine). I. Screening, taxonomy, fermentation and biological activity.