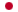
Protuboxepin A
- Structure
-

- Producing organism
- Aspergillus sp.
- Biological activity
- microtubule-stabilizing agent
- Abstract
- We reported the identification of a new oxepin-containing diketopiperazine-type marine fungal metabolite, named protuboxepin A which showed antiproliferative activity in several cancer cell lines. In this study we elucidated the mechanism by which protuboxepin A induces cancer cell growth inhibition. Here we report that protuboxepin A induced round-up morphology, M phase arrest, and an increase in the subG(1) population in tumor cells in a dose dependent manner. Our investigations revealed that protuboxepin A directly binds to α,β-tubulin and stabilizes tubulin polymerization thus disrupting microtubule dynamics. This disruption leads to chromosome misalignment and metaphase arrest which induces apoptosis in cancer. Overall, we identified protuboxepin A as a microtubule-stabilizing agent which has a distinctly different chemical structure from previously reported microtubule inhibitors. These results indicate that protuboxepin A has a potential of being a new and effective anti-cancer drug.
- References
-
- Lee SU, Asami Y, Lee D, Jang JH, Ahn JS, Oh H.: Protuboxepins A and B and protubonines A and B from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SF-5044.
J Nat Prod, 74(5): 1284-1287 (2011) [ doi: 10.1021/np100880b ]
[ doi: 10.1021/np100880b ]- Asami Y, Jang JH, Soung NK, He L, Moon DO, Kim JW, Oh H, Muroi M, Osada H, Kim BY, Ahn JS.: Protuboxepin A, a marine fungal metabolite, inducing metaphase arrest and chromosomal misalignment in tumor cells.
Bioorg Med Chem, 20(12): 3799-3806 (2012) [ doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2012.04.039 ]
[ doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2012.04.039 ] - Lee SU, Asami Y, Lee D, Jang JH, Ahn JS, Oh H.: Protuboxepins A and B and protubonines A and B from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SF-5044.